This post was prompted by a recent post at Eng-Tips.
The original problem seemed simple enough:
Im trying to wirte a formula where I imput vessel heading and datum bore heading and it tells me FWD, STBD, AFT or PORT
Now FWD and AFT are I can manage. If the difference between two headings is 45 or less then its FWD. if its greater than 135 its AFT
Between 45 or 135 is PORT or STBD depending on which way vessel turns. If vessel turns clockwise on compass then bore heading on PORT and and if anticlockwise its STBD
Anyone know how to write such a thing on excel?
For consistency the terminology used in the rest of this post will be:
- Angles are measured clockwise from North, so will always be between 0 and 360 degrees.
- The angle from the boat to the datum bore is referred to as the Reference Bearing.
- The ship’s direction of travel is referred to as the Heading
- The angle required is the angle from the Heading to the Reference Bearing, which will be divided into FWD, STBD, AFT, PORT, and back to FWD, with transitions at 45, 135, 225, and 315 degrees.
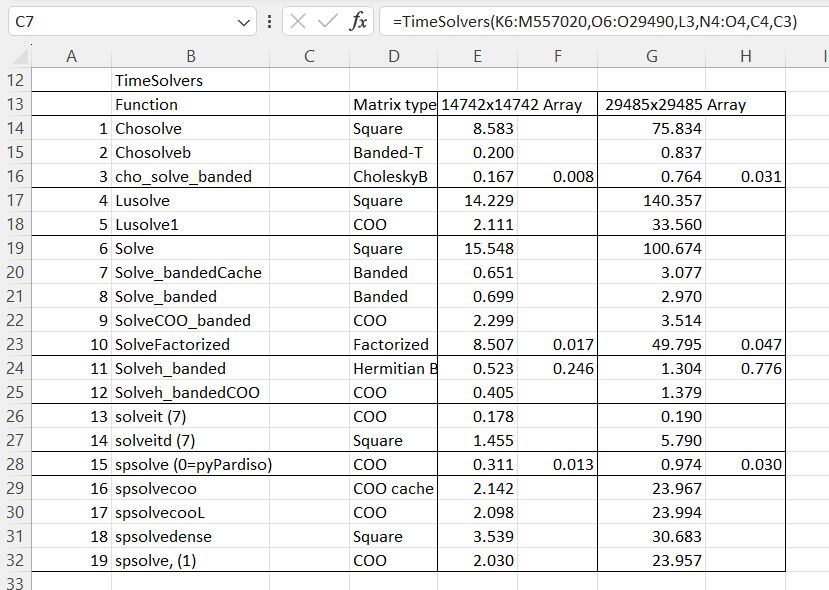
The problem is that if the angle is calculated as Ref. Bearing – Heading, it may lie between -360 degrees and 360 degrees, which makes any single formula using nested if statements very long. The simplest solution is to use a VLookup formula with a table, as in the screenshot below:

The table can be shortened by using the formula =MOD(Ref-Head, 360), which returns an angle between 0 and 360. The shortened lookup table is in my opinion the simplest solution, and the easiest to check, but two working alternatives were given in the discussion, which used a single cell formula:
- The formula in cell A16 uses =INDEX() with a list of the four direction names, and a formula using MOD() that returns a value between 1 and 4.
- The formula in cell A11 uses the sum of the Sin and Cos of Ref-Head, together with nested Ifs and ANDs.
A simpler solution using the ABS function was suggested, but this does not work when the Ref-Head angle is negative.
Finally Eng-Tips regular MintJulep provided some VBA code to plot the Reference Bearing and Heading instantly whenever one of the angles was changed:

Both spreadsheets shown above, including full open-source VBA code can be downloaded from: